
The mathematics describing the pattern observed does depend on the geometry of the grating. Describe the diffraction pattern produced by white light when. Electromagnetic radiation occurs over an extremely wide range of wavelengths, from gamma rays with wavelengths less than about 1 × 10 11 metre to radio waves measured in metres.
Which describes diffraction of light series#
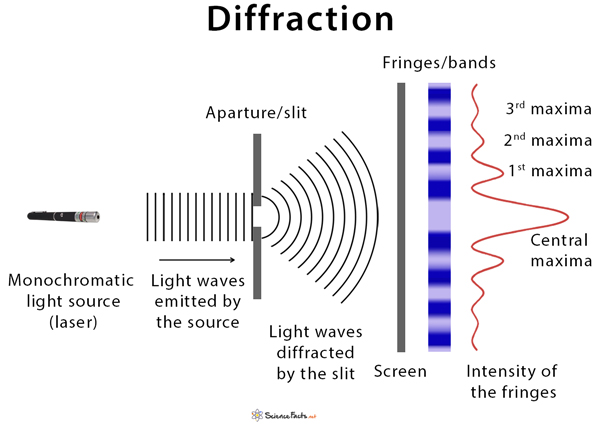
The light which will be reflected due to constructive interference depends on the wavelength and the thickness of the film (the the index of refraction in the film).Ī diffraction grating is a series of slits which we can use to create a series of spaced out fringes. White light is a mixture of different wavelengths which are diffracted each by different amounts. light, electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. You can produce the nice colored fringes that you often see on gasoline slicks or soap bubbles. When waves meet a gap or an edge in a barrier, they continue through the gap or past the edge of the barrier. Perhaps the key thing to take away from this equation is that for larger wavelengths the degree of spreading is greater.Īn interesting phenomena called thin film interference happens when light interference with itself by reflecting between surfaces of a film. So for small angles we can get away with using one equation for both of these phenomena. We can see for the double slit interference, things are similar but not exactly the same The equation for single slit diffraction can be found at hyperphysics with a nice explanation of the concepts. The definition of diffraction is the spreading of waves as they pass through or around an obstacle. Where λ is wavelength, d is the slit separation, x is the fringe spacing, and L is the distance to the screen. An alternative picture for photon diffraction had been proposed describing diffraction by a distribution of photon paths determined through a Fourier. What Is Diffraction We classically think of light as always traveling in straight lines, but when light waves pass near a barrier they tend to bend around that barrier and become spread out. Your workbook will lead you to believe you can swap the equation between these two related, but different phenomena. However, the equations which describe the location of fringes, or anti-nodes are different, and the physical underpinnings of these equations are different.

The interference arrangement is the same as that produced by the object. Interference and diffraction are different phenomena, although there are significant connection. Hologram Light diffracts in different ways when it passes across the hologram, creating both physical and artificial pictures of the item utilized to reveal the film. This is known as Young’s Principle, who first did several experiments with slits, and is well known for observing the interference of slight using a 2 slit experiment.

It appears as if the slit itself is the source of circular waves as opposed to the original source.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
